Bootstrap is a free and open-source front-end web framework for designing websites and web applications. It contains HTML- and CSS-based design templates for typography, forms, buttons, navigation and other interface components, as well as optional JavaScript extensions.

The Code-RX Blog
Creative Designs By CCW is a full service Web Development and SEO company. Our philosophy is based on providing our clients with comprehensive, all-inclusive, fully responsive web design services that include stunning designs and no hidden fees. By creating the Code-RX Blog, we hope to share some of our own techniques, while curating insights from industry experts including highlighting emerging trends, design philosophies, and the integration of cutting-edge technologies. Read a few sample blog posts below and for more detailed articles visit our blog at The Code-RX Blog
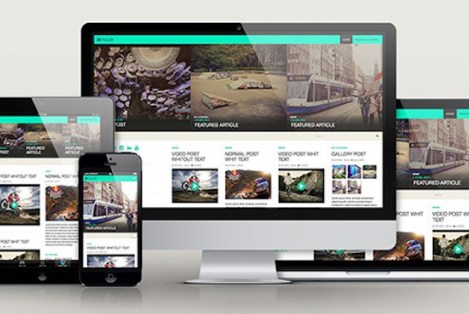
Responsive Web design is the approach that suggests that design and development should respond to the user's behavior and environment based on screen size, platform and orientation. The practice consists of a mix of flexible grids and layouts, images and an intelligent use of CSS media queries.
SEO or Search Engine Optimization is the name given to activity that attempts to improve search engine rankings. In search results Google displays links to pages it considers relevant and authoritative. Authority is mostly measured by analyzing the number and quality of links from other web pages. In simple terms, your web pages have the potential to rank in Google so long as other web pages link to them.
HTML (Hyper Text Mark Up Language) is the language used to write most web pages. Hypertext refers to links that allow the read to jump to other pages or sites or places with in the same page. Mark Up Language refers to the use of a series of tags and attributes that allow computers to speak to each other and control the flow of text.
CSS stands for cascading style sheets and it is a rule based language used to stylize mark up languages, such as HTML. CSS is intended to simplify the process of web design and can be used for styling and laying out web pages and printed materials.
Java Script is a programming language for the web that is used to change both HTML and CSS. JavaScript uses variables or containers to store data values. JavaScript can be used to change attributes, styles and elements of both HTML and CSS. JavaScript is a program language that is used in nearly 98% of all the web pages on the world wide web today.
The Crucial Need for Two-Factor Authentication in Today's Digital Landscape
December 24, 2023 in Web SecurityIn an era where our lives are increasingly intertwined with the digital realm, safeguarding our online accounts has become more critical than ever.
Passwords alone may no longer suffice to protect sensitive information from the ever-evolving tactics of cybercriminals.
This is where Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) emerges as a beacon of security, adding an extra layer of defense to our virtual identities.
Two-Factor Authentication is not just a recommended security measure; it is a necessity in our digitized world. By incorporating an additional layer of defense, individuals and businesses can significantly enhance the security of their online presence, protecting personal and sensitive information from the ever-present threat of cybercrime. Embracing 2FA is a proactive step toward a more secure and resilient digital future.
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a security process that requires individuals to provide multiple forms of identification before granting access to a system, application, or digital account. The goal is to add an extra layer of security beyond just a username and password. MFA is designed to enhance the protection of sensitive information and reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
The three main factors used in multi-factor authentication are typically:
Something You Know: This is typically a password or a PIN (Personal Identification Number). It's information that the user is expected to know.
Something You Have: This involves a physical device or token that the user possesses, such as a smartphone, security token, or smart card.
Something You Are: This refers to biometric data, such as fingerprints, retina scans, voice recognition, or facial recognition.
Meta tags are HTML elements that provide information about a web page to search engines and website visitors. These tags are placed in the head section of an HTML document and are not visible on the actual webpage. Meta tags play a crucial role in helping search engines understand the content and context of a web page, which can impact the page's search engine ranking and display in search results.
Here are some common types of meta tags:
Title Tag: Specifies the title of the web page, which is displayed on the browser's title bar or tab. It is also a crucial factor for search engine optimization (SEO).
Meta Description: Provides a brief summary of the page's content. Search engines may use this description in search results.
Meta Keywords: Historically used to specify keywords relevant to the page's content, but search engines now generally ignore this tag.
It's important to note that while meta tags are important for SEO, search engines use a variety of factors to determine a page's ranking, and content quality and relevance play a significant role.
Contact Us
Contact Creative Designs By CCW today to discuss your web design project.
We offer services through out the USA, Canada and Mexico.
- Phone:
Call 1-800 890-2208
- Email: info@creativedesignsbyccw.com
- Website: www.creativedesignsbyccw.com